1. Understanding ISO 15118
1.1 Overview of ISO 15118
ISO 15118 is an international standard that sets the framework for communication between EVs and Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE). The primary goal is to standardise the exchange of information necessary for efficient and secure vehicle-to-grid (V2G) communication, enabling functionalities such as bidirectional charging and automated data exchange.
ISO 15118 was developed collaboratively by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The joint effort began in 2010, with the aim of creating a standardised communication protocol that could support the integration of EVs into the smart grid. The first iteration of the standard, which included the Plug & Charge feature, was released in 2014. This feature, along with others, was designed to simplify the charging process and ensure secure, efficient communication between EVs and charging infrastructure.
2. Key Features of ISO 15118
2.1 Plug and Charge (PnC)
One of the standout features of ISO 15118 is Plug and Charge (PnC). PnC simplifies the EV charging process by automating authentication and payment stages. When an EV connects to a compatible charging station, the vehicle and the station communicate directly, authenticate each other, and complete the transaction securely without driver intervention. This seamless process enhances user convenience, making EV charging as straightforward as traditional refueling.
2.2 Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
Another critical aspect of ISO 15118 is its support for V2G communication, which allows for bidirectional energy transfer between the EV and the grid. This capability enables EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also to feed energy back into it. This is particularly useful for grid management, as it allows for the stabilisation of energy supply during peak demand times and the efficient utilisation of renewable energy sources. By dynamically exchanging information, the EV and the grid can negotiate optimal charging schedules, balancing the load and ensuring grid stability.
2.3 Smart Charging
Smart charging is an integral feature of ISO 15118, allowing for the adjustment of charging rates based on various parameters such as grid demand, electricity prices, and the availability of renewable energy. This ensures that the charging process is not only efficient but also environmentally friendly. Smart charging can reduce the load on the grid during peak times and take advantage of periods when renewable energy production is high, thus promoting sustainable energy usage.
3. Evolution of ISO 15118
3.1 Initial Version: ISO 15118-2
The initial version, ISO 15118-2, focused on wired communication and basic functionalities, setting the groundwork for secure and efficient communication between EVs and charging stations.
3.2 Latest Iteration: ISO 15118-20
The latest iteration, ISO 15118-20, introduces several enhancements, including support for wireless charging, improved security protocols, and multiple contract handling capabilities. These improvements are designed to accommodate the growing complexity and demands of the EV ecosystem.
4. The Role of Plug and Charge in the EV Ecosystem
4.1 Simplifying the Charging Process
Plug and Charge technology is transformative for the EV industry. By automating the authentication and payment process, PnC reduces the friction associated with charging EVs. Drivers no longer need to use RFID cards, apps, or manual payment methods. Instead, the system automatically handles these tasks, allowing for a seamless charging experience.
4.2 Stakeholders in the PnC Ecosystem
The Plug and Charge ecosystem involves various stakeholders, including:
- OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers): Equip their vehicles with the necessary hardware and software to support PnC.
- CPOs (Charging Point Operators): Deploy compatible charging stations.
- MOs (Mobility Operators): Facilitate mobility services that integrate PnC capabilities.
- Trust Service Providers: Ensure secure transactions through digital certificates.

5. Security and Trust Management in ISO 15118
5.1 Robust Security Framework
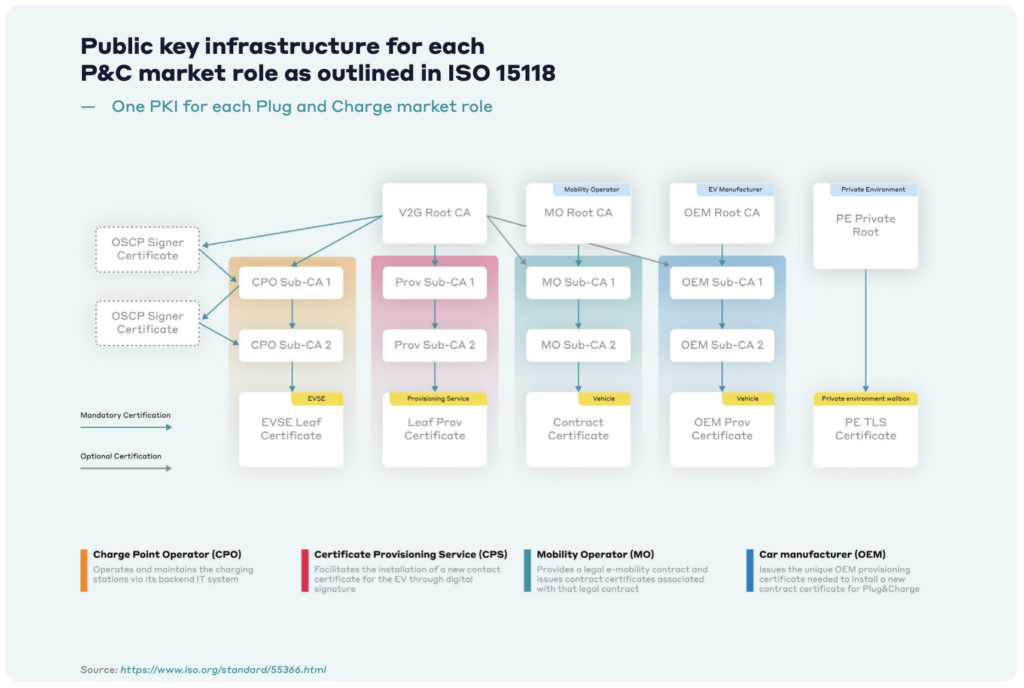
A critical component of ISO 15118 is its robust security framework, which relies on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). PKI involves the issuance of digital certificates to authenticate the identities of EVs, charging stations, and backend systems, ensuring secure communication and data exchange.
5.2 Digital Certificates
Digital certificates play a vital role in maintaining the security and trustworthiness of the PnC ecosystem. They verify the identities of entities involved in the charging process and facilitate encrypted communication, protecting against unauthorised access and data breaches. The hierarchical structure of PKI, with root, intermediate, and leaf certificates, ensures a scalable and secure authentication mechanism.
5.3 Threats and Mitigations
The increasing complexity of the EV ecosystem introduces various security threats, including unauthorised access and data interception. ISO 15118 mitigates these threats through multiple security measures, such as TLS encryption for secure communication between EVs and charging stations and certificate revocation to ensure real-time verification of certificate validity
6. Innovations and Updates in ISO 15118-20
6.1 Bidirectional Charging
ISO 15118-20 brings several new features and enhancements, including bidirectional charging. This allows EVs to supply power back to the grid, which is crucial for integrating renewable energy sources and stabilising the power grid.
6.2 Cryptographic Agility
Cryptographic agility enables the system to adapt to new cryptographic algorithms as they emerge, ensuring long-term security and resilience against evolving cyber threats.
6.3 Multiple Contract Management
The introduction of multiple contract management provides greater flexibility for EV drivers by allowing them to switch between different service providers seamlessly, enhancing user experience and expanding market opportunities.
7. Development and Implementation of Smart Charging Systems
7.1 Overview of Smart Charging Systems
Smart charging systems are essential to manage the growing demand for electricity due to the increasing number of EVs. These systems help balance electricity consumption and generation, particularly when integrating renewable energy sources that are often intermittent. The goal is to optimize charging times and rates to ensure grid stability and efficient use of resources.
7.2 Key Features of Smart Charging Systems
7.2.1 Bidirectional Communication
Smart charging systems enable dynamic information exchange between the EV and EVSE, which is crucial for efficient energy management. This communication allows for real-time adjustments in charging rates based on grid conditions and energy availability.
7.2.2 Charge Emulation Systems
Charge emulation systems, using advanced microcomputers, simulate the communication between EVs and EVSEs. These systems incorporate virtual batteries and sophisticated charging algorithms, reflecting real-world conditions and providing valuable insights into the charging process.
7.2.3 Demand Response
Smart charging systems are designed to respond to demand fluctuations in the energy grid. By adjusting charging parameters based on the availability of renewable energy, these systems help maintain grid stability and promote the use of clean energy sources.
7.3 System Architecture
The architecture of smart charging systems typically includes two main components: the EV side and the EVSE side. Each component is equipped with management codes and communication controllers that facilitate the exchange of dynamic charging parameters.
7.3.1 EV Side (EVpi)
The EV side includes a virtual battery and a management code that implements charging strategies like Constant Current (CC) and Constant Voltage (CV). This side communicates with the EVSE to ensure optimal charging based on real-time data.
7.3.2 EVSE Side (EVSEpi)
The EVSE side includes management codes for setting charging tariffs and integrating with Internet of Things (IoT) data servers. This side adjusts the charging rates based on grid conditions and renewable energy availability, ensuring efficient energy use.
8. Conclusion
ISO 15118 and its Plug and Charge feature are revolutionizing the EV charging landscape. By standardizing communication protocols and enhancing security, ISO 15118 facilitates seamless, efficient, and secure charging experiences. The integration of smart charging systems, based on ISO 15118, further enhances the sustainability and reliability of the EV ecosystem. As adoption continues to grow, these advancements will play a crucial role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.

