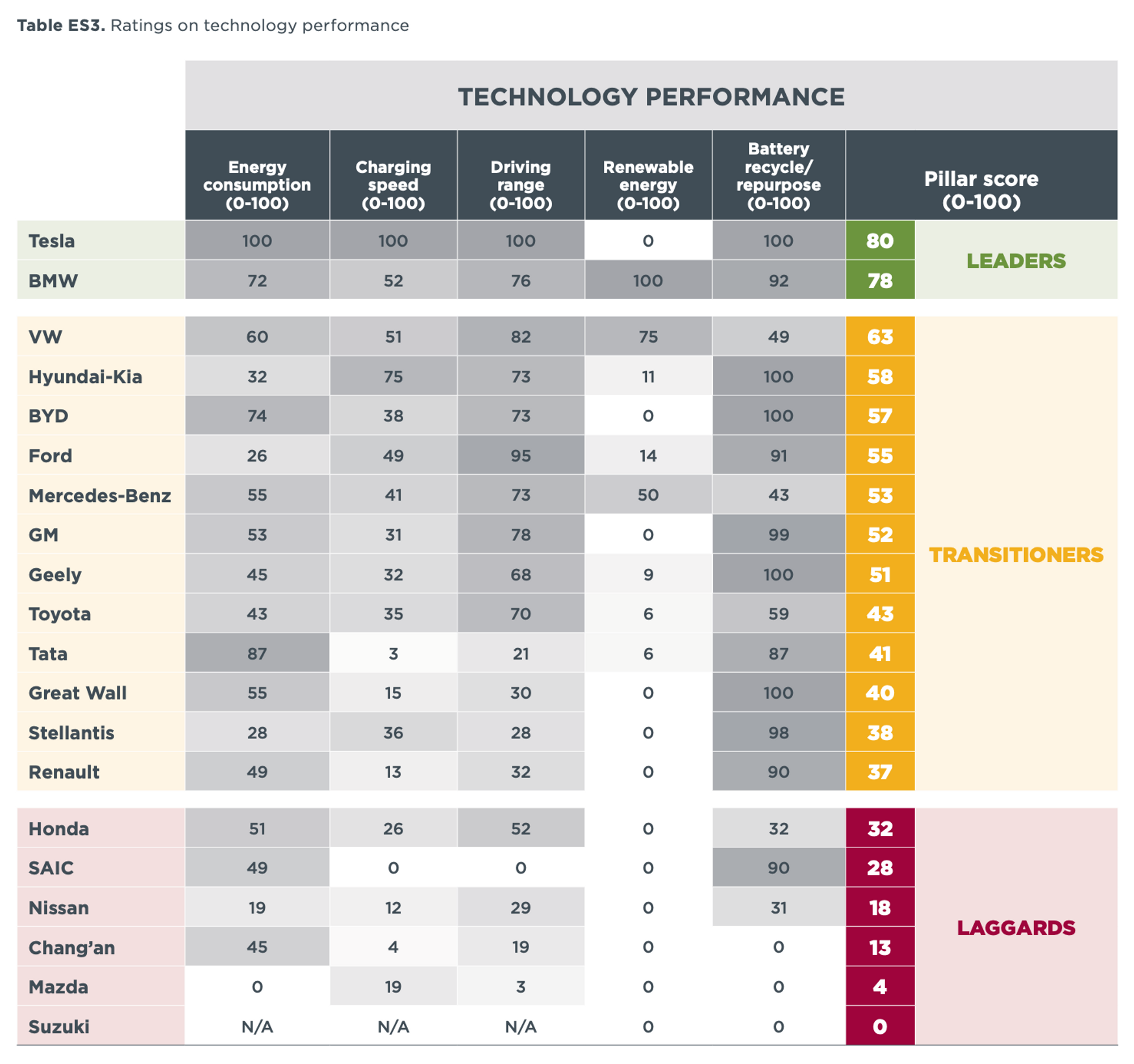
The report, which focuses on key metrics and criteria, presents a comprehensive assessment of automakers’ progress, categorizing them into three groups: leaders, transitioners, and laggards, based on their scores in various categories.
At the forefront of this transition are two standout manufacturers: Tesla and BYD. Tesla, known for producing exclusively ZEVs since its inception, excels in key technology attributes such as energy consumption, charging speed, and driving range. Meanwhile, BYD is on the verge of achieving a 100% ZEV sales share, though it still has a significant number of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) in its fleet.
The report highlights the diversity of strategies employed by automakers in the ZEV transition. Several companies, including Chang’an, Geely, SAIC, Stellantis, and VW, may lag in current ZEV sales but are making substantial progress by offering a wide range of ZEV models across various vehicle classes.
Furthermore, some automakers are focusing on sustainability in their manufacturing processes, with BMW, VW, and Mercedes-Benz leading the way by transitioning to 100% renewable electricity for production.
Looking ahead, the report emphasizes the need for accelerated progress. Only half of the evaluated automakers have reached a 10% or higher ZEV sales share, while the Paris Agreement’s climate goals call for a 77% ZEV sales share by 2030.
The report also points out areas for improvement, such as enhancing technology features like energy consumption, driving range, and charging speed, as well as addressing battery production sustainability and recycling.
Interestingly, only a handful of automakers, including Stellantis, BMW, GM, Renault, and Nissan, explicitly tie executive compensation to ZEVs, indicating room for incentivizing sustainable practices at the highest levels.
Notably, the six lowest-rated automakers include five headquartered in Japan and one in India, signaling the need for a more robust strategy for ZEVs with clear targets and investments.
The ICCT’s report distinguishes itself as a data-driven, in-depth evaluation focused solely on ZEV transition efforts, setting it apart from broader ESG ratings. The report is grounded in quantitative and transparent data, providing a detailed methodology and specific metrics tailored to ZEVs.
The ICCT plans to update and publish this rating annually, reflecting the ongoing progress made by automakers as they innovate and invest in a ZEV future. As the industry evolves, the report’s framework and data will also adapt to incorporate new insights and real-world data on energy consumption, driving range, and charging.
In conclusion, The ICCT’s report serves as a vital resource for stakeholders interested in the transition to ZEVs, shedding light on the progress and challenges faced by global automakers in their pursuit of a more sustainable transportation future.
Source: The Global Automaker Rating 2022 | The ICCT