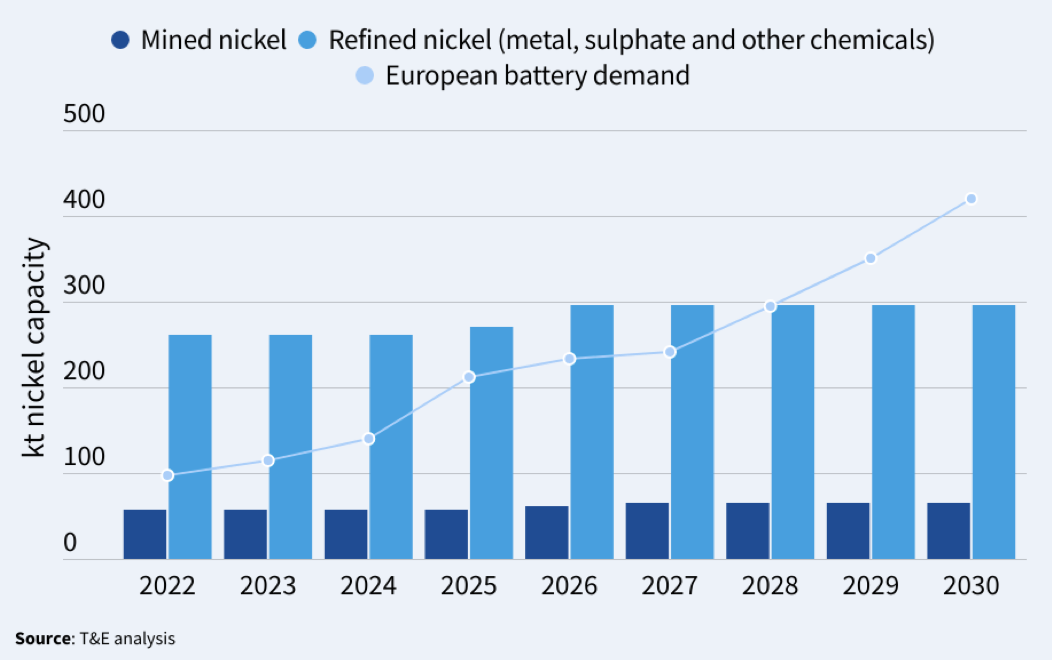
By 2030, nickel-containing chemistries are projected to dominate half of the global market, indicating a steep rise in demand. Indonesia is poised to be a major player, expected to supply 60% of the mined output and 40% of the refined output by the end of the decade, thanks to its rapid ascendancy as a nickel powerhouse.
Europe is not far behind in tapping into its nickel reserves, with potential mining capacities projected to fulfill 16% of the region’s demand for EVs and energy storage systems. Refined nickel sulphate capacities, vital for battery production, could meet 15% of the future demand, with a possible expansion of up to 70% if metal capacities are redirected towards this sector.
However, nickel mining and refining are not without environmental implications. T&E’s report highlights the substantial carbon footprint associated with these processes. Minviro’s analysis indicates a wide variance in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across production sites, influenced by energy sources and production technologies. Facilities leveraging renewable energy and hydrometallurgical technologies like bioheap leaching and pressure oxidation have the lowest carbon footprints.
The report emphasises the potential of renewable energy to reduce emissions by up to 40%. Moreover, it advocates for zero-carbon chemicals in processing, decarbonised mining vehicles, optimised logistics, and efficient ore processing techniques to mitigate the industry’s GHG emissions.
T&E underscores the necessity of policy intervention to clean up nickel production. This includes boosting renewables in the energy mix, defining low emission nickel refining routes, and mandating best available technologies for environmental conservation. Global standards like the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) are recommended to enhance environmental and social stewardship.
For Europe, the focus is on establishing a local battery value chain under the EU Critical Raw Materials Act. The strategy involves supporting strategic projects adhering to stringent standards and providing targeted funding (e.g., via the EU Innovation Fund). Furthermore, collaboration and investment in sustainable projects abroad are essential for fostering mutually beneficial trade relationships with nickel-rich countries.
This report by Transport & Environment not only underscores the growing importance of nickel in the EV industry but also provides a blueprint for sustainable sourcing practices crucial for the success of the global green transition.
Source: Paving the way to cleaner nickel | Transport & Environment