Selected reports
- V2G: A critical technology to enable the energy transition | CRA & Hubject
- Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Trends from the Alternative Fueling Station Locator: First Quarter 2022 | NREL
- Deploying charging infrastructure to support an accelerated transition to zero-emission vehicles | ZEVTC
V2G: A critical technology to enable the energy transition
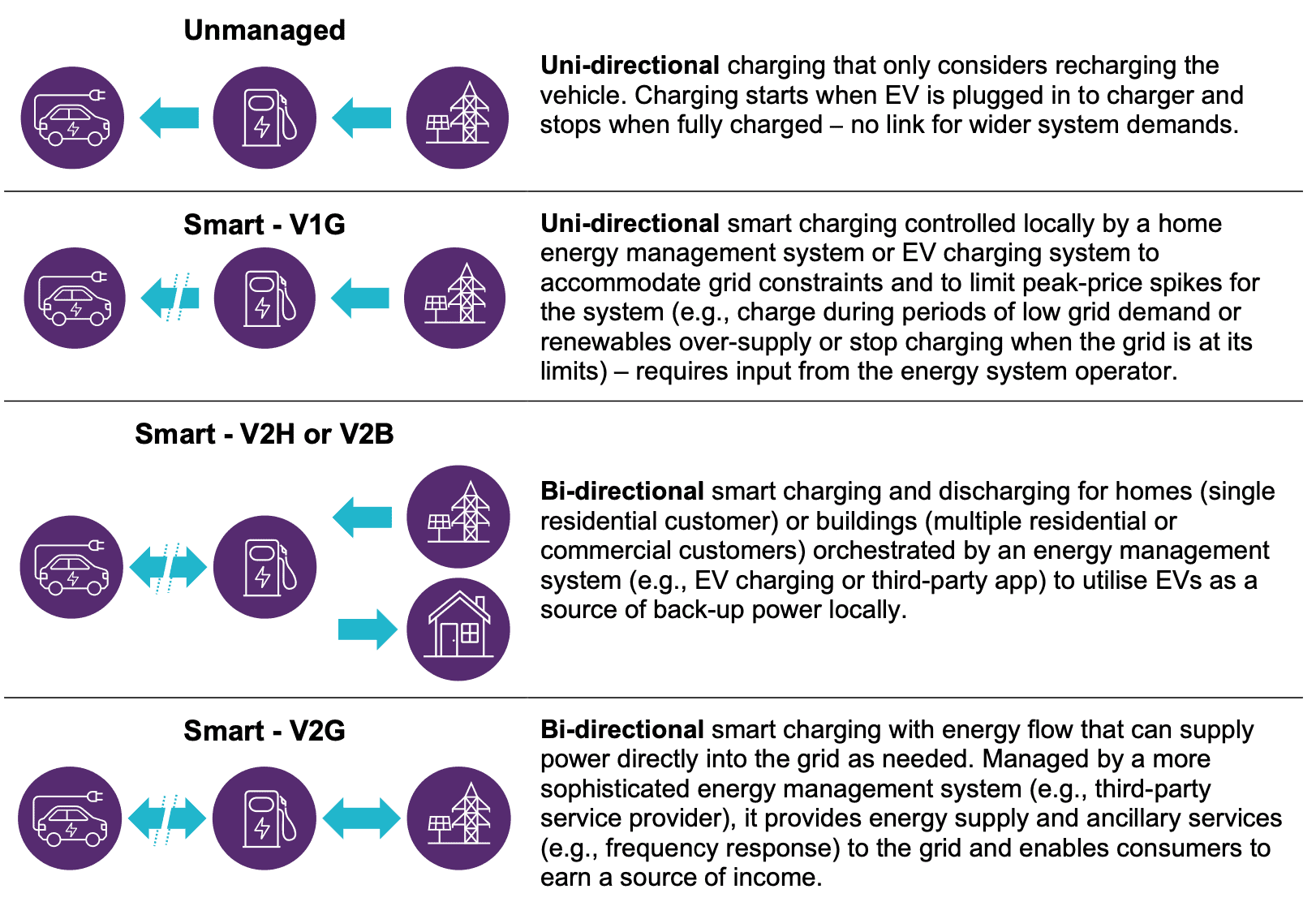
Without smart charging, the exponential increase in electric vehicles (EVs) and the infrastructure required to support their charging would cause significant issues for the energy networks. For instance, uncontrolled grid charging of many EVs would require hefty capital investments to expand capacity and prevent overloading. However, EV battery smart charging technologies have the potential to increase grid flexibility, reduce system costs, and reduce emissions in addition to potentially alleviating grid capacity issues if they are widely implemented.
This research explains several smart charging kinds, examines the history of V2G, explores present issues, and assesses V2G’s possibilities in the future. Additionally, it evaluates the rationale for deploying EVs to supply energy services, identifies the long-term repercussions of failing to accomplish V2G, and presents value pools and alternative business models for industry participants.
V2G: A critical technology to enable the energy transition | CRA & Hubject
The state of EV charging infrastructure in the United States
The Alternative Fuelling Station Locator provided by the U.S. Department of Energy lists all public and private non-residential alternative fueling stations in North America. Ethanol (E85), biodiesel, compressed natural gas, electric vehicle (EV) charging, hydrogen, liquefied natural gas, and propane stations are currently tracked by the Station Locator. EV charging continues to have the fastest-growing infrastructure and technological change of all these fuel kinds.
This report compares two distinct infrastructure needs scenarios for 2030 with the existing condition of charging infrastructure. This information is meant to aid in the understanding of the fast evolving EV charging infrastructure environment by transportation planners, policymakers, researchers, infrastructure developers, and others.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Trends from the Alternative Fueling Station Locator: First Quarter 2022 | NREL

Ramping up EV charging infrastructure deployment
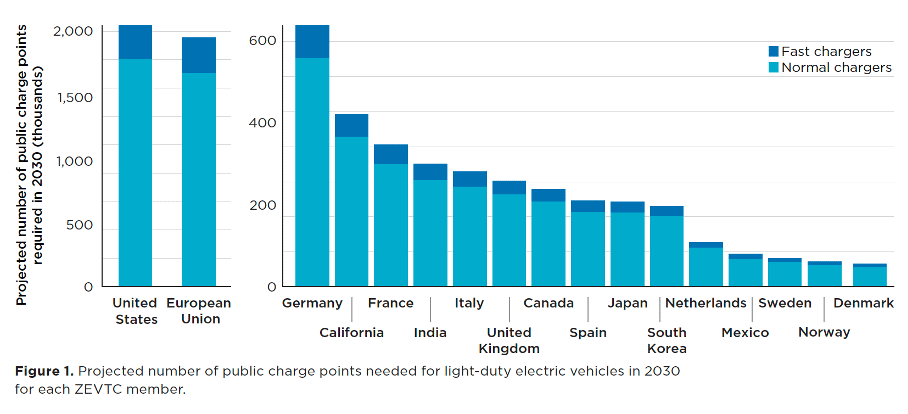
Many attendees of COP-26 anticipated that light and heavy zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs) will be widely used. This, however, is only possible if charging infrastructure is introduced at the rate and scale outlined in the Global Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) for Zero-Emission Medium- and Heavy-Duty Vehicles (ZEMHDV) and the ZEV Declaration.
This report uses modelling to determine how much charging infrastructure will be required in member jurisdictions of the Zero Emission Vehicles Transition Council (ZEVTC) through 2030 to support a quick switch to ZEVs. This report also includes information on policy strategies to hasten the implementation of this infrastructure.
Deploying charging infrastructure to support an accelerated transition to zero-emission vehicles | ZEVTC