Haryana’s Strategic Position in EV Adoption
Haryana, a key player in India’s industrial growth and urbanization, emerges as an ideal subject for this study. The state is strategically positioned, surrounding the capital territory of Delhi on three sides and home to over 25 million people. With ambitious targets for phasing out fossil-fueled government and public vehicles, Haryana’s draft EV policy, implemented since July 2022, focuses on developing extensive public and private charging facilities.
State of Public Charging Infrastructure
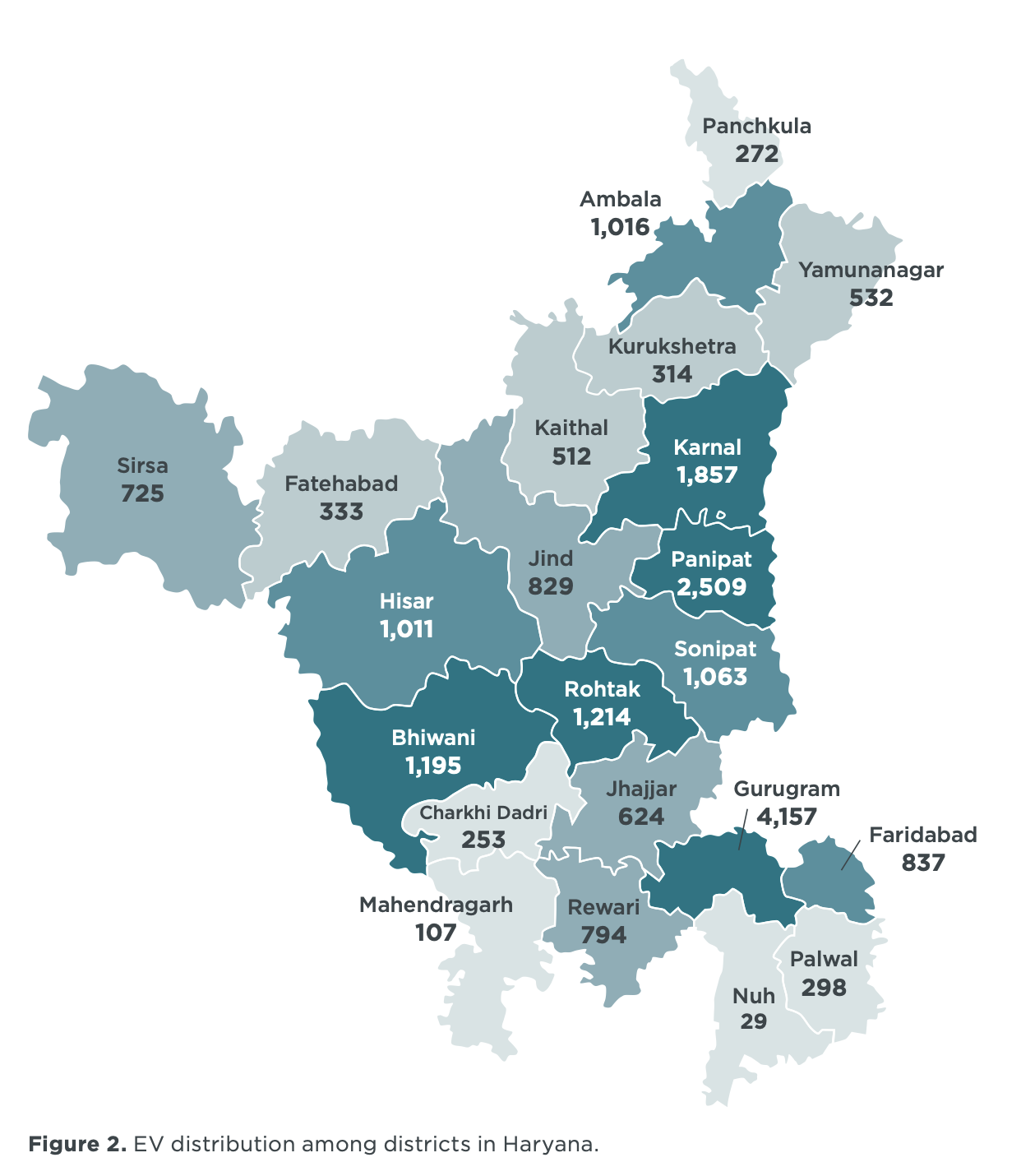
The study reveals that as of 2022, Haryana possesses 454 public EV charging stations, accounting for 2.9% of India’s total charging infrastructure. This distribution is concentrated primarily in urban districts like Gurugram and Faridabad. Gurugram leads with 25.1% of the state’s EVSEs (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), followed by Faridabad with 7.6%.
However, the report highlights a significant imbalance in the distribution of these facilities across the state. While some districts like Nuh, Palwal, and Mahendragarh boast a higher number of charging stations relative to the number of EVs, other districts lag behind, indicating a need for more equitable infrastructure development.
Challenges and Opportunities
One of the primary challenges in Haryana’s EV adoption is the uneven distribution of fast and slow chargers. The state currently has a higher proportion of slow chargers, which could impact the feasibility of using EVs, especially for commercial purposes. Only 1.3% of chargers in Haryana are fast chargers, underscoring a significant area for improvement.
The study suggests several measures for enhancing Haryana’s charging infrastructure. These include establishing benchmarks for minimum distance to charging stations, increasing the number of charging stations per 1,000 EVs, and boosting the proportion of fast chargers, particularly in districts with higher EV usage.
Conclusion
This ICCT briefing is a clarion call to action, underscoring the need for a robust and well-distributed EV charging network in Haryana. As the state progresses with its EV policy, the development of an efficient charging infrastructure becomes paramount. This case study not only sheds light on Haryana’s current readiness but also provides a roadmap for other Indian states to follow suit in their journey towards a sustainable, EV-powered future.
Source: India’s Public EV Charging Infrastructure Readiness – A Case Study of Haryana State | The ICCT