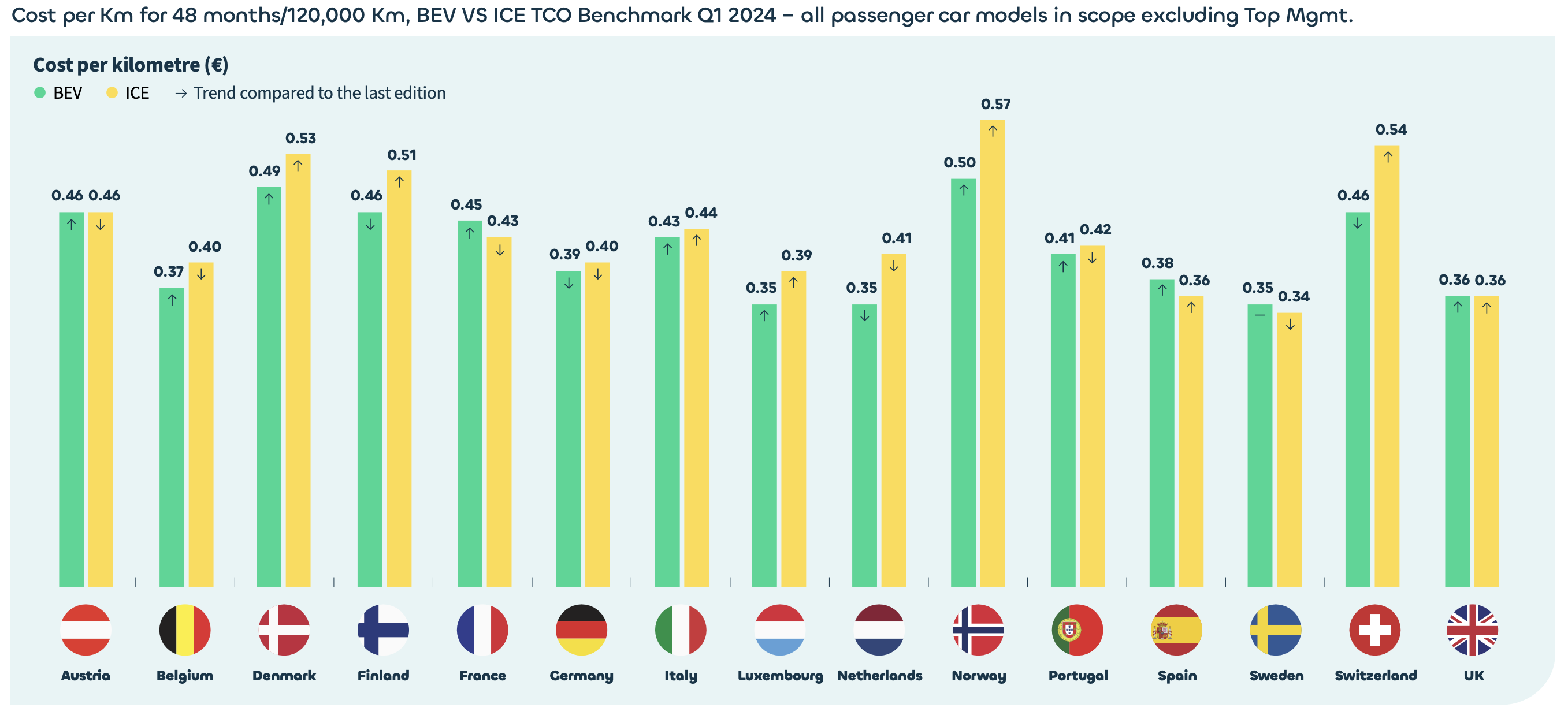
In these countries, the TCO for BEVs has become higher than for ICE vehicles. This shift is due to the end of government subsidies and rising energy costs. For example, France ended BEV benefits for corporate customers, and Germany unexpectedly stopped BEV acquisition subsidies. These changes have made ICE vehicles more cost-competitive in the short term. Meanwhile, the UK and Austria have seen BEV TCO return to parity with ICE vehicles.
Despite these challenges, BEVs still offer long-term financial advantages in several markets. The increasing variety of available models and the rapid expansion of charging infrastructure are key drivers in maintaining BEV competitiveness. Countries like the Netherlands and Norway are leading the way in infrastructure development, significantly lowering the overall cost of BEV ownership through improved charging accessibility.
The report also highlights the volatility of BEV pricing, influenced by geopolitical trade tensions, fluctuating energy prices, and changing regulatory environments. This volatility requires fleet managers to adopt flexible strategies, such as multi-cycle leasing and rightsizing vehicle choices, to manage costs effectively. Additionally, exploring alternative powertrains and implementing mobility budgets can further optimise fleet expenses.
While the TCO for BEVs faces certain headwinds in specific markets, the broader trend remains positive. Driven by regulatory support, technological advancements, and growing consumer acceptance. Fleet managers must stay informed and adaptable to navigate this dynamic landscape successfully, leveraging comprehensive insights and tailored strategies to achieve sustainable and cost-effective mobility solutions.
Source: Ayvens

EV Policy Europe 2010 – 2025: Why the ‘deer in the headlights’ strategy puts its Automotive future at risk
The European Commission’s 16 December announcement to ease the 2035 CO₂ reduction targets marks a pivotal moment for Europe’s automotive sector. After more than a decade in which the industry