The Power of Charge: Understanding Charger Speed
When Electric Vehicles first entered the market, consumers clamored for a battery range that could rival that of traditional combustion engines, often citing the 500-mile mark as the magic number. However, a paradigm shift is underway as consumers realize that raw range isn’t everything, especially if electric cars can replenish their energy swiftly. Today, it’s about the fusion of range and rapid charging capabilities.
Beneath the Surface: Unraveling Charging Speed Metrics
Electricity’s speed is quantified in kilowatts (kW), while capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Despite its straightforward appearance, charging speed’s complexity lies within the interplay of voltage and amperage. The charger itself is just one player; the car’s onboard charger and battery management system significantly influence how fast an EV can charge.
AC vs. DC: The Charging Highway
Public charging stations commonly fall into two categories: Level 2 and Level 3. Level 2 stations provide AC (alternating current) electricity at 220-240 volts—akin to a residential washer or dryer hookup. However, the charger within the vehicle limits the charging speed. EV batteries thrive on DC (direct current) electricity, which requires an onboard converter. Here, the onboard charger’s speed reigns supreme, determining charge speed for both home and public Level 2 charging.
DC Fast Charging: Turbocharging the Charge
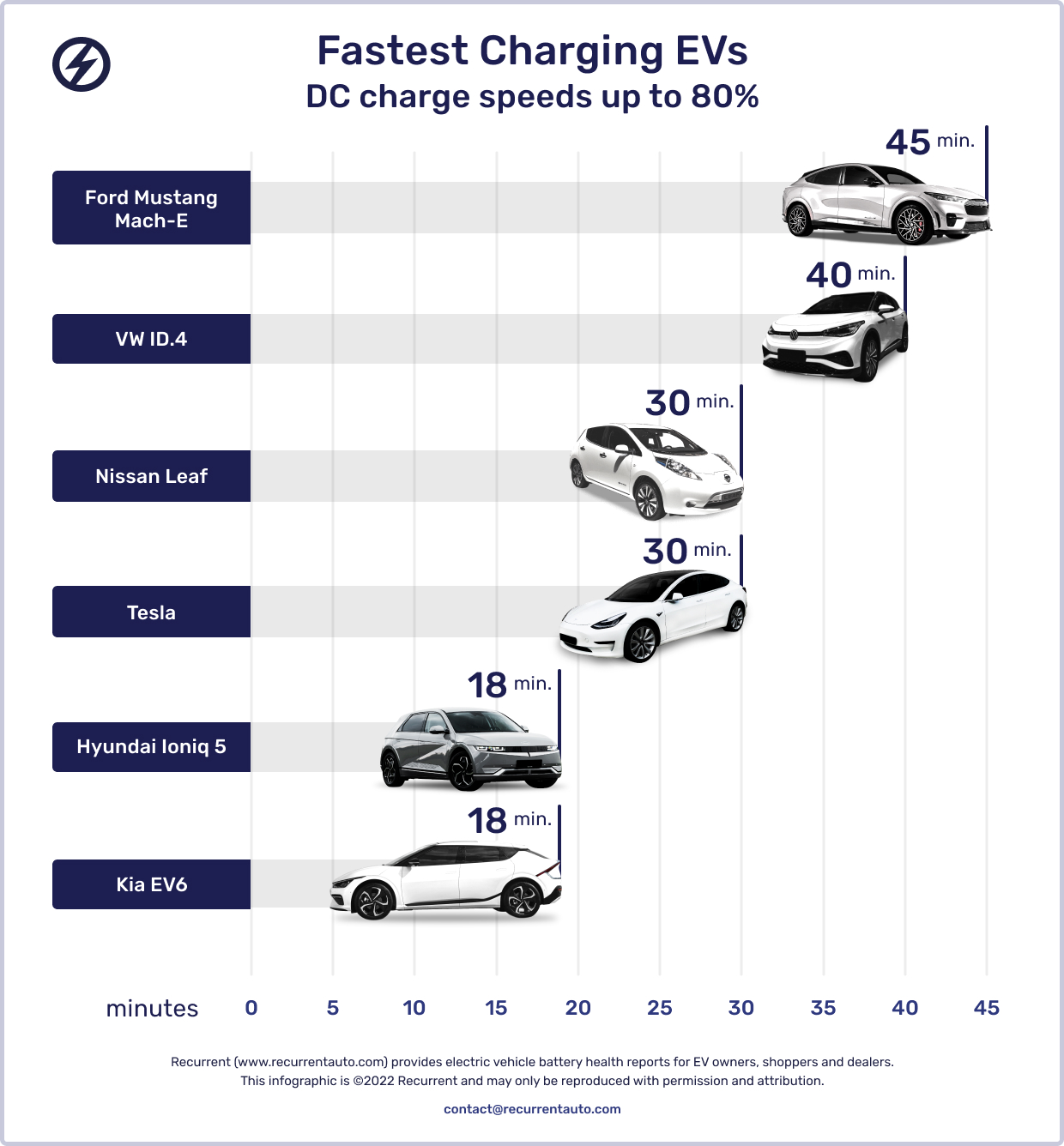
For expedited charging on road trips or quick top-offs, Level 3 (DC fast charging) stations are indispensable. By bypassing the onboard charger, direct current flows directly into the battery, facilitating rapid charging. These stations can rejuvenate an EV from 20% to 80% in about 45 minutes, offering a game-changing solution for time-sensitive charging needs.
Deciphering the Charge Speed Limits
The velocity of DC fast charging is governed by an electric vehicle’s battery management system (BMS). This intricate system protects the battery by monitoring factors like temperature and charge level, adjusting charging speed accordingly. Cold temperatures prompt the BMS to delay fast charging to avert battery damage. The BMS also curbs charging speed at extremely low or high battery states to prevent wear and tear.
Advertisement vs. Reality: Navigating Advertised Charging Speeds
Car manufacturers advertise peak charge speeds under ideal conditions, yet real-world scenarios often differ. Temperature, grid amperage, battery state of charge, and charger capacity can alter the actual charging time. Therefore, considering the full charge curve provides a more accurate picture of the charging experience.
Source: recurrent