The heart of modern LIBs lies in their electrode design, with High Energy (HE) electrodes emerging as a critical component. Automotive High Energy Lithium-Ion Batteries (HE-LIBs) are navigating a challenging landscape where energy density, crucial for longer vehicle ranges, often conflicts with the need for high power density, essential for fast-charging capabilities. Optimising these factors involves a series of engineering trade-offs, impacting everything from electrode porosity to the choice of conductive materials.
Recent trends indicate a shift towards slightly thicker electrodes for HE-LIBs, promising higher energy densities and cost efficiencies. However, this comes with its own set of challenges, necessitating innovations in slurry casting and other manufacturing techniques. The industry is also exploring novel concepts like template-based structures and additive manufacturing to enhance electrode performance.
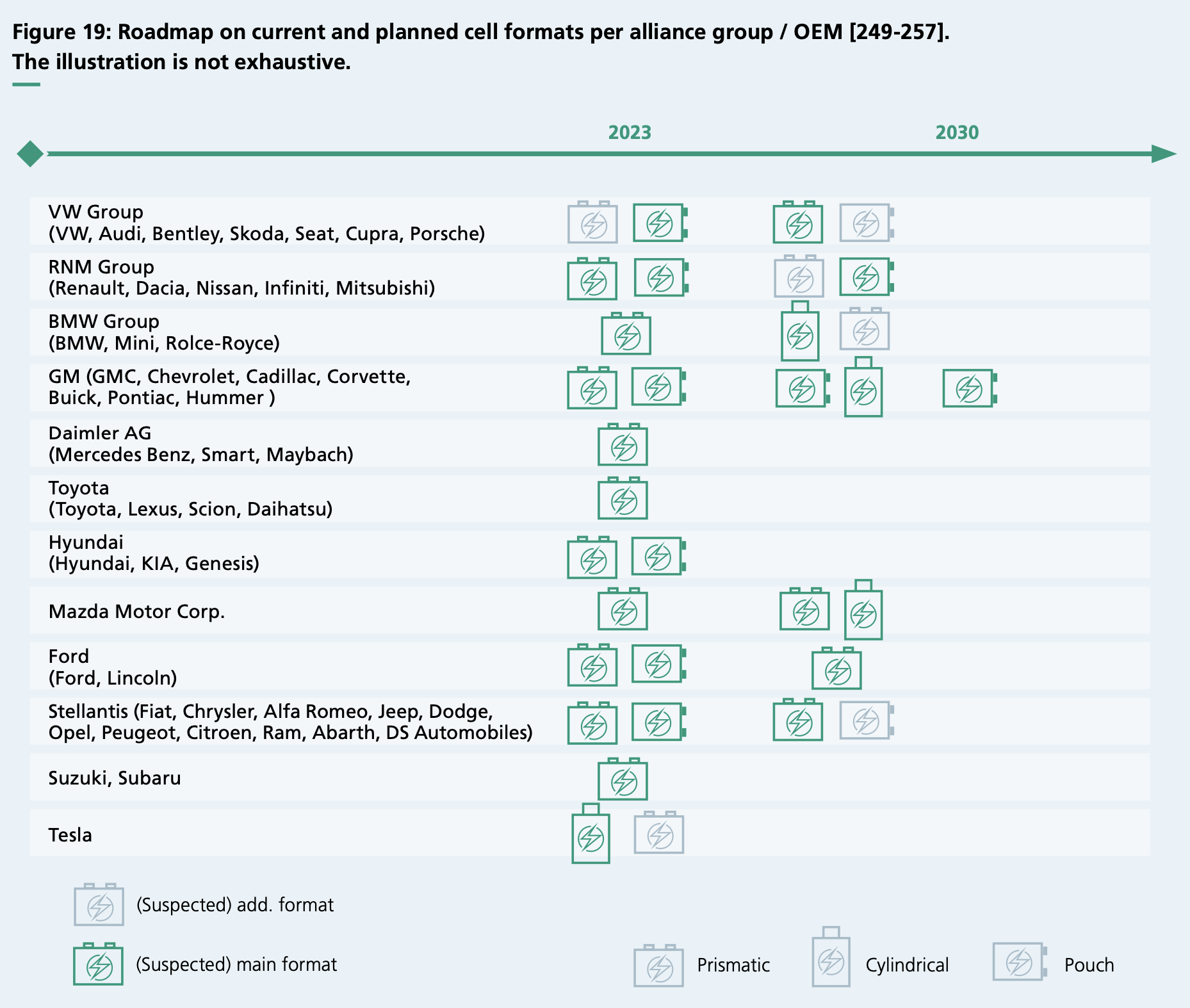
When it comes to electrode assembly, the report notes a strong influence on overall cell performance. Techniques like winding and stacking are evolving, with industry giants indicating a future preference for single-sheet stacking or stack-winding in prismatic and pouch cells, while cylindrical cells might continue utilising winding concepts.
The roadmap doesn’t just highlight technological advancements; it also sheds light on strategic shifts among Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and cell suppliers. There’s a trend towards consolidating cell formats to leverage economies of scale and facilitate easier sourcing. Large prismatic cells and blade-type cells are gaining traction, with several leading automotive manufacturers like VW, Ford, and BMW announcing shifts towards these formats. These cells offer a blend of high capacity and mechanical stability, making them increasingly popular.
Cylindrical cells aren’t left behind, with Tesla’s adoption of the 4680 cell format setting a precedent for higher energy and power density. Several other OEMs and manufacturers are following suit, indicating a broader acceptance and potential standardisation of this format in the industry.
In the realm of energy densities, the industry is ambitiously marching towards the 1,000 Wh/l and 400 Wh/kg milestones. Both cylindrical and pouch cells are at the forefront of this race, with next-generation cells expected to significantly surpass current energy density levels. Prismatic cells, once lagging, are rapidly catching up, with advancements in high-energy cathodes and silicon-enhanced graphite anodes.
The report’s findings emphasise that the future of lithium-ion batteries is not just about technological advancements but also about strategic partnerships and industry standards. Companies like BMW, Mercedes, Toyota, and CATL, among others, are actively investing in new cell designs and production capabilities. These collaborations and innovations are setting the stage for a new era in energy storage, promising more efficient, cost-effective, and powerful batteries that could revolutionise the automotive industry and beyond. As we move forward, the LIB roadmap presents a future where our energy solutions are not just more advanced but also more aligned with the growing demands of sustainability and efficiency.
Source: lithium ion battery roadmap | Fraunhofer ISI