Among the four energy-consuming sectors, transportation stands out as having the most significant potential for electrification. The transportation sector currently relies heavily on non-electrified energy sources, with gasoline-powered vehicles dominating the landscape. In fact, motor gasoline usage for light-duty vehicles accounts for a staggering 51% of energy consumption in this sector alone.
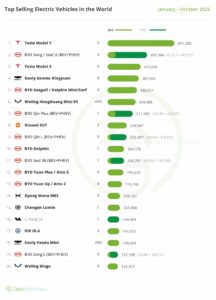
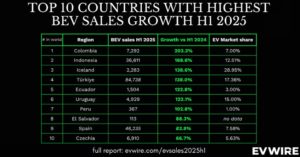
However, the tide is turning. The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming the transportation sector and offering a promising path towards electrification. While the share of electricity in the sector’s energy use remains relatively low at 0.2%, the increasing adoption of EVs indicates significant room for growth and further electrification in the coming years.
But electrification is not limited to transportation alone. The infographic also highlights the residential and commercial sectors, where space heating constitutes the largest energy use. Although natural gas is the primary energy source for space heating in these sectors, electricity is increasingly being used for space cooling, refrigeration, lighting, and computing equipment. Advancements in residential solar systems, heat pumps, and energy efficiency measures are contributing to the electrification drive in homes and offices.
The industrial sector, which accounts for one-third of U.S. energy consumption, poses more significant challenges for electrification due to its heavy reliance on fossil fuels. Industries like chemicals, mining, and refining are major consumers of oil and gas. However, the integration of renewable energy and technologies like electric arc furnaces and electric boilers hold promise for advancing industrial electrification while reducing emissions.
Experts believe that electrification is a key building block for achieving economy-wide decarbonization. By replacing fossil-fuel powered systems with electric alternatives, there is an opportunity to power these systems with low-carbon electricity from renewable sources and nuclear power. When combined with a decarbonized power sector, increasing electrification across sectors can lead to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
As the world continues to grapple with the urgent need to address climate change, the United States’ push towards electrification could be a significant step in the right direction. While challenges remain, the potential for widespread EV adoption and the transition to electric alternatives in other sectors present a promising pathway to a greener and more sustainable future.
Source: NPUC, Visual Capitalist