1. What is Eichrecht?
Eichrecht, officially known as the Mess- und Eichgesetz (MessEG) and Mess- und Eichverordnung (MessEV), is a German calibration law applied to a range of measuring instruments, including electricity meters at EV charging stations. Introduced to ensure transparency and accuracy in commercial transactions, Eichrecht mandates that all public and semi-public charging stations must have certified energy meters. These meters must be regularly calibrated and deliver accurate, unaltered measurements of the electricity consumed during an EV charging session.
1.1 Purpose of Eichrecht in EV charging
In everyday life, consumers expect clarity and fairness in billing—whether filling a car with gasoline or charging an electric vehicle. Eichrecht seeks to bring that same transparency to EV charging. The law ensures that EV drivers can see exactly how much energy they used, what they were charged, and confirm the accuracy of this data independently. By imposing strict regulations on the calibration of energy meters, Eichrecht protects consumers from overcharging and guarantees a fair and trustworthy billing process.

2. How Eichrecht works in practice
The Eichrecht framework covers a wide range of activities, from how charging stations measure energy consumption to how that data is processed and presented to the consumer. Let’s dive into how it operates at the technical level.
2.1 Calibration of energy meters
At the heart of Eichrecht is the calibration of the energy meters. Under this law, the meters used in public EV charging stations must be certified by Germany’s National Metrology Institute (Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, or PTB). These certified meters are regularly calibrated to ensure that the energy readings displayed and billed correspond precisely to the actual energy consumed. Without this periodic calibration, a charging station is not legally allowed to charge consumers for energy usage.
2.2 Secure transmission of charging data
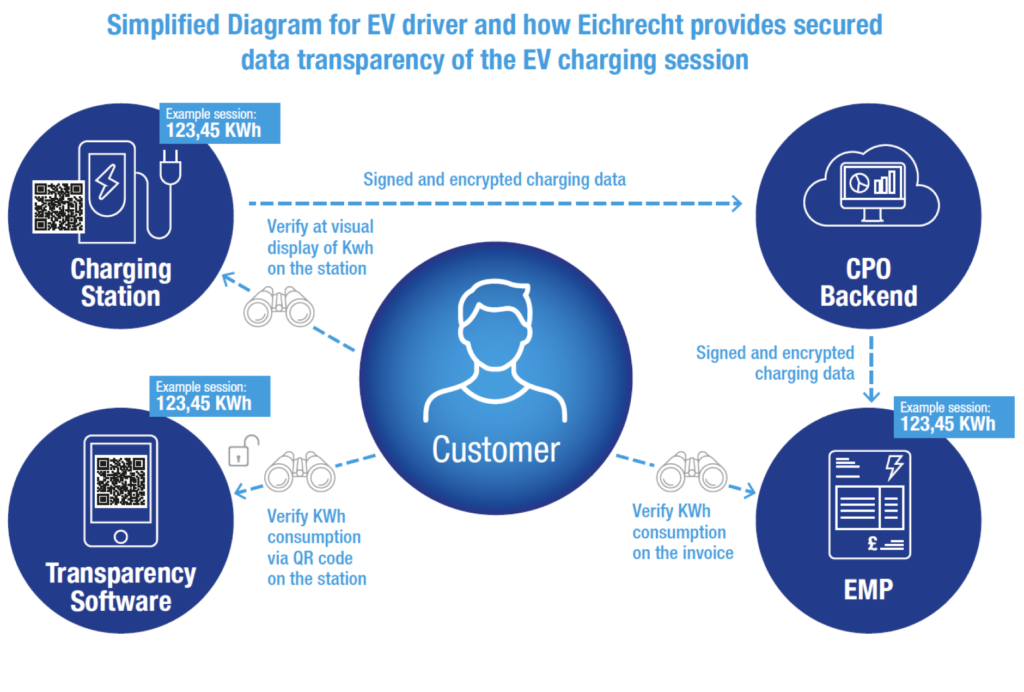
Once energy consumption is recorded, the data is encrypted to prevent tampering. A unique digital signature and public key are attached to each transaction, which is stored securely. The charge point operator (CPO) then transmits this encrypted data to the e-mobility service provider (EMSP), ensuring that the information remains unchanged during the entire process. This transparency enables consumers to trust the transaction process, as they can verify the details of their charging session independently.
3. Transparency and consumer verification
One of the key pillars of Eichrecht is the ability for consumers to independently verify their energy consumption and ensure that they are being billed accurately. This is done through a process that ensures data transparency and security at each step of the billing process.
3.1 The role of transparency software
Consumers can use independent verification tools such as the Transparency Software for E-mobility (S.A.F.E.) to confirm that the data recorded during their charging session has not been tampered with. This software allows users to cross-reference the digital signature provided by the charging station, ensuring that the amount of energy consumed, as displayed on their invoice, matches the actual energy delivered during their session. In this way, consumers can verify both the accuracy and integrity of the data they receive.
3.2 The importance of a digital signature
The digital signature generated during each charging session is crucial for protecting data integrity. It allows consumers and authorities to authenticate the transaction, ensuring that no third party—such as a charge point operator—has modified the recorded energy values. The public key associated with each transaction can be accessed by the consumer, adding another layer of transparency and security.
4. Who must comply with Eichrecht?
Eichrecht compliance is mandatory for all public and semi-public EV charging stations in Germany, but the law doesn’t apply equally across all types of charging infrastructure. Understanding where it applies is essential for stakeholders in the EV market.
4.1 Public and semi-public charging stations
For public and semi-public charging points—such as those located at shopping centers, parking lots, or along highways—Eichrecht is non-negotiable. These stations must use calibrated meters to measure and display the exact energy used in real time. The operators of these charging stations are also required to provide transparent and detailed billing to the consumer, including itemized charges that show the energy consumed, additional fees (such as parking), and the price per kWh.
4.2 Workplace charging
If employees are required to pay for workplace charging, the station must also comply with Eichrecht. This ensures that employees are billed fairly for the energy they use during working hours, and that their billing data is secure and verifiable.
4.3 Exemptions for private home chargers
Private home chargers are exempt from Eichrecht. Because these chargers are used for personal, non-commercial purposes, they are not subject to the same level of regulatory scrutiny. Homeowners are free to install non-calibrated energy meters, as they are not required to bill third parties for electricity consumption.
5. Challenges and solutions for Eichrecht compliance
Meeting the requirements of Eichrecht can be technically complex, especially for charge point operators (CPOs) and manufacturers. However, solutions are available to ensure compliance while maintaining flexibility and scalability.
5.1 Calibration and certification of meters
One of the biggest challenges for charging station manufacturers is ensuring that their meters comply with Eichrecht’s strict calibration standards. Companies like EVBox and Alfen have developed proprietary solutions, such as smart adapters and certified energy meters, to meet these requirements. These meters are designed to prevent tampering while offering compatibility with transparency software like S.A.F.E., which allows users to verify their transactions independently.
5.2 The role of software in compliance
Software plays a vital role in achieving and maintaining Eichrecht compliance. There are Solutions that offer CPOs the tools they need to manage transactions, store encrypted charging data, and ensure the integrity of that data throughout the billing process. This software helps charging station operators meet the transparency and security requirements mandated by Eichrecht, while also providing consumers with confidence in the accuracy of their bills.
6. Eichrecht’s impact on the EV market
Germany’s strict calibration law has implications not just for consumers but also for the broader EV market, influencing how manufacturers, CPOs, and e-mobility providers operate within the country.
6.1 Ensuring fair competition
By setting a standard for accurate billing, Eichrecht promotes fair competition among charging station operators. Consumers are empowered to compare prices between different providers, ensuring that no one is unfairly charged or given inaccurate information. This, in turn, fosters a healthy marketplace where consumers can choose the best service based on clear and transparent pricing.
6.2 Implications for future regulation in Europe
Eichrecht is one of the most advanced calibration laws for EV charging in the world, and other European countries are expected to follow suit. As electric vehicle adoption increases, we are likely to see similar regulations enacted across the European Union, ensuring consistent standards for transparency and fairness in EV charging. Eichrecht serves as a model for how these laws can protect consumers while encouraging market growth.
7. Conclusion
Eichrecht has set a high standard for EV charging transparency and billing accuracy in Germany. By ensuring that all energy meters are calibrated, data is encrypted, and consumers can verify their transactions independently, this law fosters trust and fairness in the growing electric mobility sector. As more countries consider implementing similar regulations, Eichrecht’s influence will likely expand, helping to shape a more transparent and consumer-friendly EV charging market across Europe.

